O que é que aparece primeiro: gigante vermelha, anã branca ou supernova?
Estamos a falar aqui de coisas distintas. O fator preponderante é a massa inicial da estrela. Consideremos, como exemplo, o nosso Sol. Atualmente ele é definido como sendo uma estrela da Sequência Principal. No futuro (daqui a alguns milhares de milhões de anos) irá transformar-se numa gigante vermelha com um raio que poderá atingir a região onde a Terra descreve a sua órbita. Depois as camadas mais externas dessa gigante irão soltar-se dando origem a uma nebulosa planetária. No centro ficará uma pequena estrela muito densa e muito quente designada por anã branca.
Estrelas como o Sol não explodem em supernova. Para isso a massa inicial da estrela terá de ser no mínimo cerca de 8 vezes superior à massa do Sol. Essas estrelas começam a sua vida como gigantes (ou supergigantes) azuis. No final da sua vida explodem (podendo passar também por uma fase de gigante vermelha) em supernova dando origem a uma estrela de neutrões ou a um buraco negro (se a massa inicial da estrela for superior a cerca de 40 massas solares).
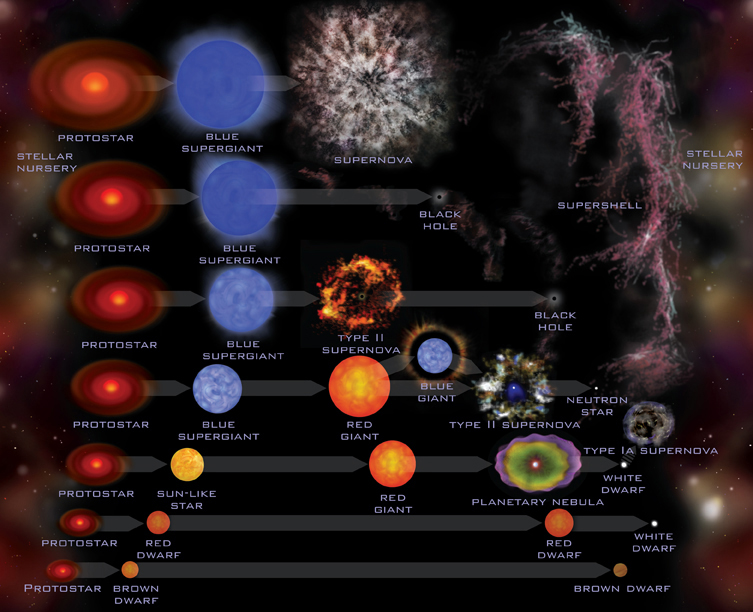
Diferentes etapas da evolução estelar / Different stages in the evolution of a star
[http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2007/sn2006gy/sn2006gy_newline.jpg]
What comes first: red giant, white dwarf or supernova?
Here we are talking about distinct things. The
preponderant factor is the initial mass of the star. We consider, for example,
or Sun. At the moment it is defined as a star that belongs to the Main Sequence.
In the future (in about 5000 million years) it will turn into a red giant with a
radius that may reach the region where earth describes its orbit. After that the
most external layers of that giant will be released giving origin to Planetary
Nebulae. In the centre will remain a small very dense and hot star called a
white dwarf.
Stars like our Sun do not explode as supernova. For
that to happen the initial mass of the star must have a minimum of 8 times the
mass of the Sun. Those stars start their life as blue giants (or super-giants).
At the end f their life they explode (they can also a red giant phase) in
supernova giving origin to a neutron star or a black hole (if the initial mass
of the star is about 40 solar masses).

